The subscapularis muscle is key for shoulder stability and internal rotation of the arm. It also assists in bringing the arm to the body’s midline. Understanding what the subscapularis does helps recognize its role in daily movement and maintaining shoulder health.
Key Takeaways
- The subscapularis muscle is crucial for internal rotation, shoulder stability, and adduction of the arm, significantly impacting both daily activities and sports.
- Injuries to the subscapularis, such as tendonitis or tears, can severely affect shoulder mobility, making prompt diagnosis and treatment essential for recovery.
- Rehabilitation for the subscapularis includes targeted exercises, stretching techniques, and treatments like dry needling to restore function and prevent injuries.
The Role of the Subscapularis
The subscapularis muscle plays a pivotal role in the complex biomechanics of the shoulder. As one of the primary rotator cuff muscles, its main function is to mediate the internal rotation of the arm. This action is crucial in many daily activities, such as reaching across the body or performing a tennis serve. But that’s not all; the it also assists in adduction, bringing the arm closer to the body’s midline.
Beyond its role in movement, the subscapularis muscle is essential for maintaining shoulder stability. It generates a significant portion of the force around the glenohumeral joint, contributing to over half of the total force in this area. This muscle’s ability to stabilize the joint helps prevent dislocations and other injuries, making it indispensable for both athletes and everyday individuals alike.
Anatomy of the Subscapularis
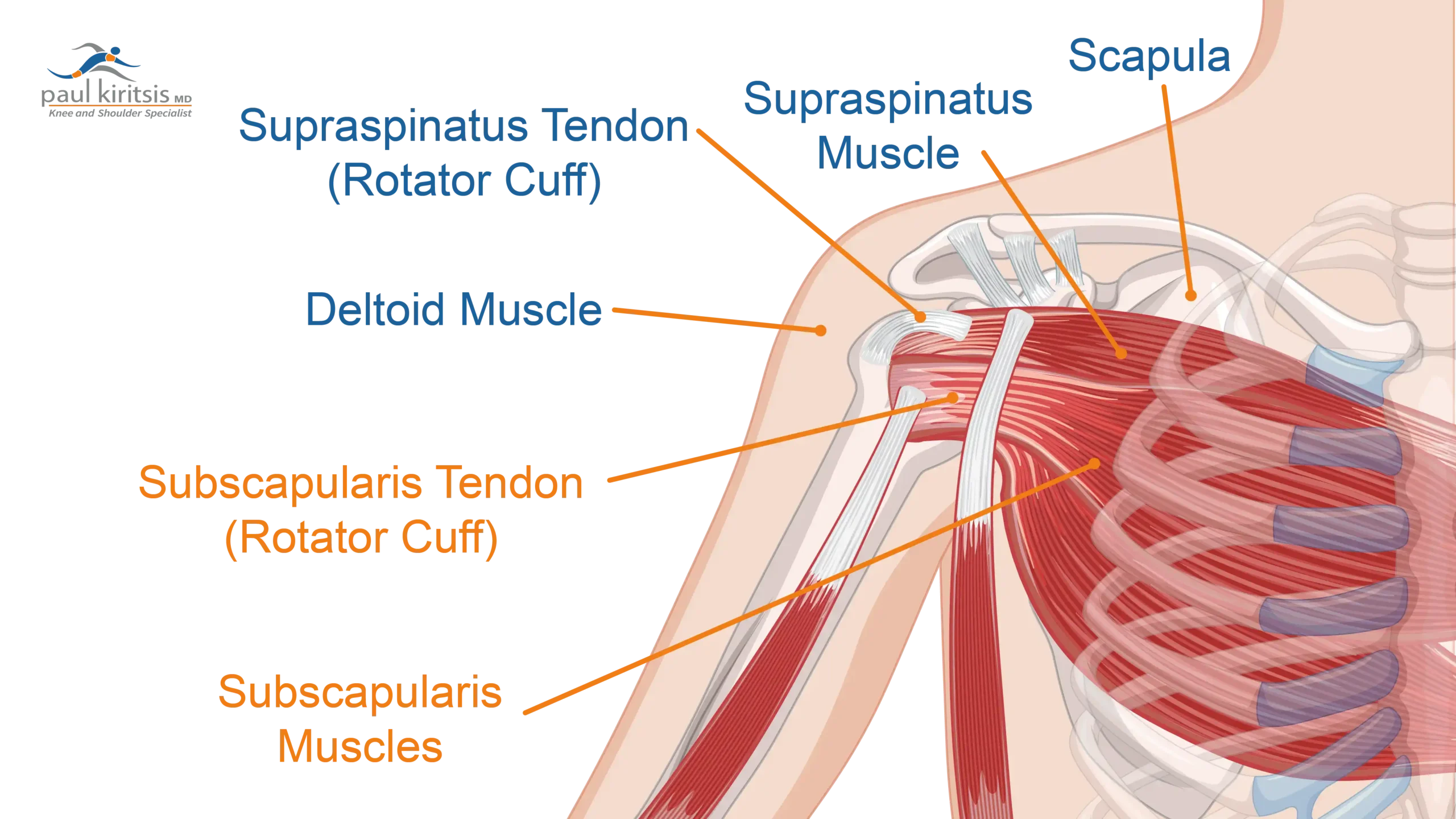
The subscapularis muscle lies strategically positioned on the anterior surface of the scapula, or shoulder blade, ensuring its effectiveness in shoulder mechanics. This large, triangular-shaped muscle is aptly named ‘subscapularis’ because it lies beneath the scapula. Its location allows it to perform critical functions in shoulder movement and stability.
Understanding the anatomy of the subscapularis muscle involves exploring its origin and insertion points, its relations with other structures in the shoulder, and its innervation and blood supply. Each of these aspects contributes to the muscle’s ability to function effectively within the rotator cuff.
Origin and Insertion
The subscapularis muscle originates from the subscapular fossa. This fossa is a broad, shallow depression located on the anterior surface of the scapula. This origin provides a strong base for the muscle fibers to extend across the shoulder joint. The muscle then inserts at the lesser tubercle of the humerus and the anterior part of the articular capsule. These insertion points enable the muscle to mediate internal rotation and stabilize the shoulder.
The placement allows it to effectively pull the humerus towards the body’s midline, facilitating internal rotation. This anatomical arrangement also enables the muscle to provide a stabilizing force during various movements, ensuring the shoulder joint remains secure and functional.
Relations with Other Structures
As one of the four rotator cuff muscles, the subscapularis plays a significant role in the stability and function of the shoulder joint. Its primary task is to medially rotate the arm towards the body’s midline, a movement essential for many daily activities. Additionally, it helps stabilize the humeral head within the glenoid cavity, preventing dislocation during dynamic arm movements.
The subscapularis muscle’s relationship with other structures in the shoulder, such as the humeral head and glenoid cavity, underscores its importance in maintaining shoulder stability. By working alongside the other rotator cuff muscles, the subscapularis ensures that the shoulder joint operates smoothly and efficiently.
Innervation and Blood Supply
The subscapularis muscle receives its nerve supply from the upper and lower subscapular nerves, branches of the brachial plexus. This innervation is crucial for the muscle’s ability to contract and perform its functions. The primary blood supply for the subscapularis comes from the subscapular artery, ensuring the muscle has the necessary nutrients and oxygen to maintain its activity.
Functional Movements
The subscapularis muscle is integral to several functional movements of the shoulder. Its primary role is in internal rotation, but it also significantly contributes to shoulder stability and the adduction of the arm. These movements are essential for various daily activities and sports, highlighting the muscle’s importance in overall shoulder function.
Understanding these functional movements helps us appreciate how the subscapularis muscle works to maintain shoulder health and performance. This knowledge is crucial for anyone looking to improve their shoulder mechanics, prevent injuries, or rehabilitate from shoulder issues.
Internal Rotation
The primary action of the subscapularis muscle is to internally rotate the arm, drawing the humerus towards the body’s midline. This movement is essential for a wide range of activities, from reaching across the body to performing athletic maneuvers. When the subscapularis muscle contracts, it causes the humerus to rotate medially, enabling these actions.
The effectiveness of internal rotation depends on the positioning of the arm. For instance, when the arm is raised, the subscapularis helps draw the humerus forward and down, ensuring smooth and controlled movements. This function underscores the muscle’s versatility and importance in various arm positions.
Shoulder Stability
The subscapularis muscle is crucial for maintaining shoulder stability, particularly as a part of the rotator cuff. It helps center the humeral head within the glenoid cavity, preventing dislocations and ensuring the shoulder joint remains secure during dynamic movements. This stabilizing function is vital for both everyday activities and high-demand sports.
By creating concavity compression, the subscapularis muscle prevents the humeral head from slipping out of place. This ability to stabilize the shoulder joint makes the muscle indispensable for maintaining shoulder health and preventing injuries.
Adduction of the Arm
While the primary role of the subscapularis muscle is internal rotation, it also assists in adducting the arm. This action involves bringing the arm closer to the torso, a movement essential for many daily tasks and athletic activities. The subscapularis muscle plays a key role in this movement, particularly when the arm is positioned in the plane of the scapula.
In addition to adduction, the subscapularis muscle can aid in shoulder extension when the arm is correctly positioned. This versatility highlights the muscle’s importance in various arm movements and its contribution to overall shoulder function.
Clinical Significance
Injuries to the subscapularis muscle can lead to significant functional impairments, affecting shoulder mobility and strength. Conditions like tendonitis and tears are common, often resulting from overuse or trauma. These injuries can cause considerable shoulder pain and impact an individual’s ability to perform daily activities.
Understanding the clinical significance of the subscapularis muscle helps in recognizing and addressing these injuries promptly. For patients who require shoulder replacement, I’ve actually made it a focal point of the my Precision Shoulder Replacement surgery and have a patent-pending repair technique in an effort to enhance surgical outcomes.
Common Injuries
Common injuries involving the subscapularis muscle include tendonitis and a subscapularis tear. Tendonitis is often caused by overuse or repetitive strain, leading to inflammation and pain during shoulder movements. Tears of the subscapularis tendon can result from acute injuries or chronic degeneration, significantly impacting shoulder function.
Regular stretching and maintaining flexibility are helpful for preventing these injuries. By incorporating proper stretching techniques, individuals can reduce the risk of injuries and maintain shoulder health.
Diagnostic Tests
Diagnostic tests play a crucial role in identifying injuries to the subscapularis muscle. The bear hug test, for instance, is specifically designed to evaluate tears and is more sensitive than other common tests. This sensitivity makes it a valuable tool for accurately diagnosing subscapularis injuries.
Other tests, like the lift-off test and the belly press test, are also used to diagnose subscapularis injuries. These tests help clinicians determine the extent of the injury and develop appropriate treatment plans.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for subscapularis injuries vary depending on the severity of the condition. Conservative treatments include rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications, which are often effective for low-demand patients. For more severe injuries, surgical intervention may be necessary, typically performed arthroscopically to minimize recovery time.
In cases of irreparable subscapularis tears, tendon transfers are sometimes performed to restore shoulder function and stability. These advanced surgical techniques highlight the importance of proper diagnosis and treatment for maintaining shoulder health.
Subscapularis in Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a vital role in the recovery and rehabilitation of subscapularis injuries. Initial treatment often involves conservative measures such as rest, NSAIDs, and physical therapy to reduce inflammation and promote healing. Physical therapy is crucial for restoring strength and flexibility, helping patients regain full shoulder function.
Incorporating specific exercises and stretching techniques into a physical therapy regimen can significantly improve outcomes. Understanding the appropriate exercises and techniques is essential for effective rehabilitation and long-term shoulder health.
Rehabilitation Exercises
Rehabilitation exercises for the subscapularis muscle focus on strengthening and improving flexibility. Rotating weights and using resistance bands are effective methods for targeting the muscle. Internal Rotation with a resistance band, for example, strengthens the shoulder by bringing the arm across the body against resistance.
Other exercises, such as the Pendulum exercise and Prone Horizontal Abduction, help stretch and strengthen the subscapularis tendon. These exercises are essential components of a comprehensive rehabilitation program, promoting recovery and preventing future injuries.
Stretching Techniques
Stretching techniques, such as Passive Internal Rotation and using a towel behind the back, help improve flexibility in the subscapularis muscle. These stretches are crucial for maintaining shoulder health and preventing injuries.
By incorporating these techniques into a regular routine, individuals can enhance their shoulder’s range of motion and overall function.
Summary
Understanding the subscapularis muscle’s role in shoulder mechanics, functional movements, and its clinical significance is crucial for maintaining shoulder health. From its anatomical details to its importance in physical therapy, this muscle plays a vital role in our daily activities. By taking care of the subscapularis through proper exercise and stretching, we can prevent injuries and ensure long-term shoulder function.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary function of the subscapularis muscle?
The primary function of the subscapularis muscle is to facilitate internal rotation of the arm. This is essential for various movements and stability of the shoulder joint.
What are common injuries associated with the subscapularis muscle?
Common injuries associated with the subscapularis muscle include tendonitis and tears, often due to overuse or trauma. Addressing these issues early can help prevent further complications.
How is a subscapularis muscle injury diagnosed?
A subscapularis muscle injury is diagnosed using specific tests such as the bear hug test, lift-off test, and belly press test, which help evaluate the functionality of the muscle. These tests are crucial for an accurate assessment of the injury.
What are the treatment options for subscapularis injuries?
For subscapularis injuries, treatment options include conservative methods such as rest and physical therapy, as well as surgical interventions for more severe cases. Prioritizing early intervention can lead to better outcomes.
How can physical therapy help in recovering from a subscapularis injury?
Physical therapy can significantly aid recovery from a subscapularis injury by providing targeted exercises and stretching techniques that strengthen the muscle and enhance flexibility. This tailored approach helps restore function and reduces the risk of re-injury.