Wondering how long it takes for a shoulder injury to heal? Recovery time depends on many factors, including the type and severity. Mild sprains typically heal in weeks, while severe injuries like rotator cuff tears might take many months. In this post, we’ll explore the expected healing times for common shoulder injuries and factors that influence recovery.
Key Takeaways
- Shoulder injury healing times vary widely, with minor injuries often healing in weeks and more severe injuries taking months to over a year.
- Recovery times can depend on factors such as the severity of the injury, the type of injury, and individual health factors.
- Treatment options range from nonsurgical methods to surgical interventions for severe cases, with post-treatment rehabilitation playing an important role in recovery.
Healing Time for Different Types of Shoulder Injuries
Shoulder injuries encompass a wide range of conditions, each with its own recovery timeline. From mild sprains to severe rotator cuff tears, understanding typical healing times can be helpful in setting realistic recovery goals.
The exact recovery duration depends on obtaining an accurate diagnosis and following a personalized treatment plan. In the following subsections, we’ll explore some of the most common shoulder injuries, their treatment strategies, and expected recovery times.
Rotator Cuff Injury Recovery
Rotator cuff tears frequently affect individuals who perform repetitive shoulder movements. A torn rotator cuff can cause significant shoulder pain and instability. Other symptoms may include weakness, limited range of motion, and clicking or popping sounds (crepitus).
Recovery timelines often depend on the severity of the tear. For many individuals, partial rotator cuff tears can improve within weeks to months with proper treatment. Severe rotator cuff injuries may require surgical intervention, with recovery times extending from many months to a year.
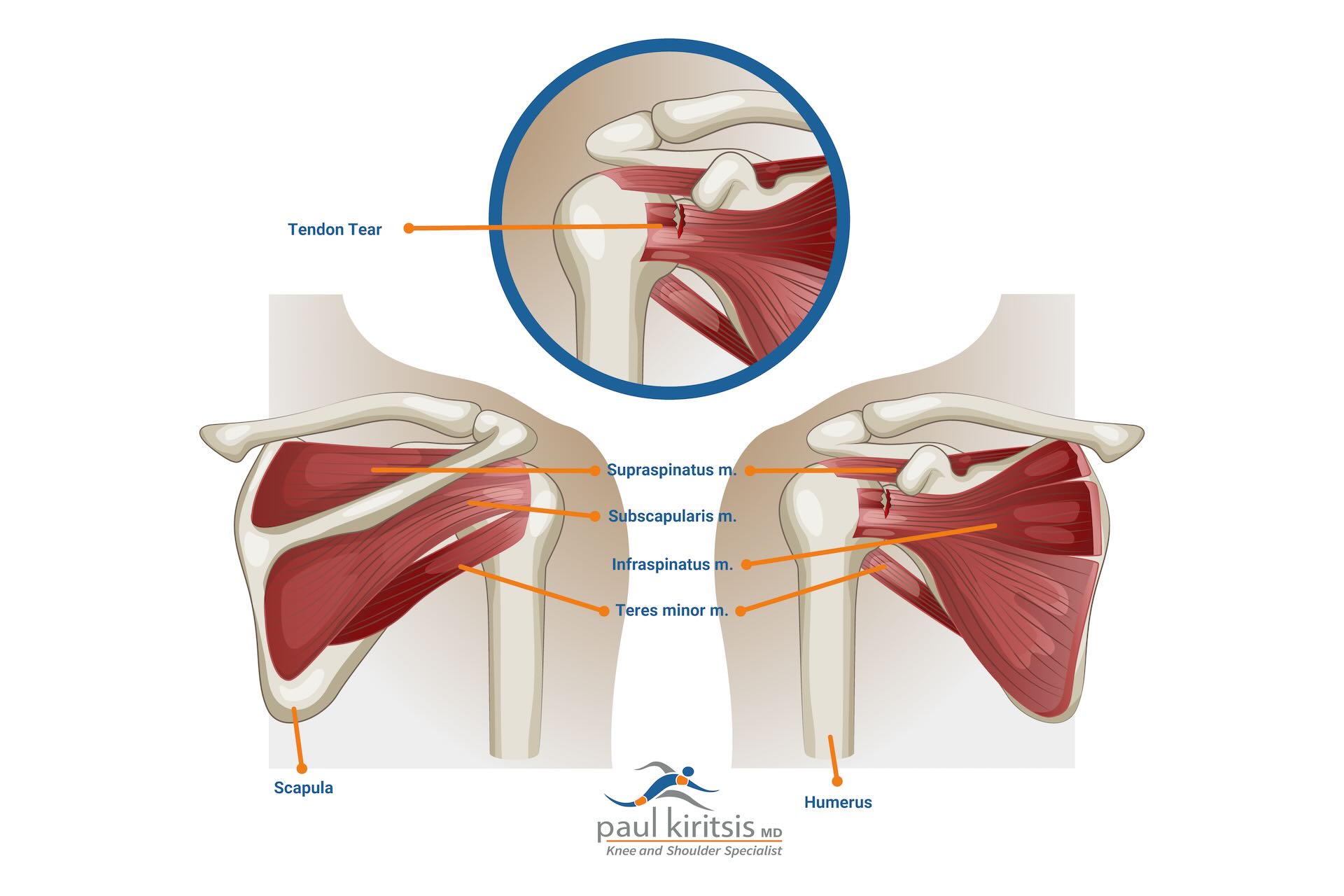
Nonsurgical treatments may include rest, physical therapy, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and corticosteroid injections. These treatments focus on reducing inflammation, easing shoulder pain, and restoring mobility. For severe cases, procedures such as arthroscopic repair or reverse shoulder replacement may be recommended to improve function.
Post-surgical care plays a key role in recovery after rotator cuff surgery. Steps typically include wearing a sling for around six weeks, avoiding forceful use of the shoulder during healing, and physical therapy. These steps support healing and reduce the risk of re-injury.
Shoulder Sprain Healing Duration
Shoulder sprains generally result from overstretching or tearing ligaments, and they vary in severity and recovery time. Mild shoulder sprains generally heal within a couple of weeks with adequate rest and rehabilitation. However, more severe sprains can take several weeks to months to fully recover, depending on the extent of the ligament damage. Performing appropriate rehabilitation exercises and avoiding aggravating activities are typically important for recovery.
Dislocated Shoulder Recovery Time
A dislocated shoulder occurs when the upper arm bone pops out of the shoulder joint, often causing immediate and intense shoulder pain. The initial treatment generally involves immobilizing the shoulder, applying ice to reduce swelling, and seeking medical attention to reposition the joint.
Recovery time for a dislocated shoulder can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the severity of the dislocation. Physical therapy is often recommended to help rebuild muscle strength and joint stability and ultimately surgery may be necessary.
Factors Influencing Shoulder Injury Recovery
Several factors influence the recovery time from shoulder injuries, including the type and severity of the injury, the patient’s age, and the chosen treatment methods. The following subsections will delve into each of these factors in detail, providing insights into how they impact the healing process.
Severity of the Injury
The severity of a shoulder injury is an essential factor in determining recovery time. More extensive injuries usually necessitate longer recovery periods due to the greater extent of tissue damage and the complexity of the healing process.
Age and Healing Speed
In many cases, age can play a role in the healing speed of shoulder injuries. Younger individuals typically experience a quicker healing process that allows them to return to their regular activities sooner. Older adults often face longer recovery times due to decreased blood circulation, slower metabolism, and potential underlying health conditions.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
Rehabilitation and physical therapy are key components in the recovery process for shoulder injuries. In many cases, engaging in a structured rehabilitation program can enhance recovery speed and functional outcomes, particularly after surgical procedures. Early engagement in physical therapy can often address specific weaknesses, promote better healing outcomes, and prevent the exacerbation of the injury.
Treatment Options for Shoulder Injuries
Treatment options for shoulder injuries range from conservative nonsurgical methods to surgical interventions. The choice of treatment often depends on the severity of the injury and the patient’s overall health.
Nonsurgical treatments, such as physical therapy and lifestyle modifications, are typically the first line of defense. However, severe injuries may require surgery to restore full function and alleviate shoulder pain. An experienced shoulder specialist can evaluate the injury and help guide the most appropriate treatment plan.
Nonsurgical Treatments
For many patients, nonsurgical treatments can be effective for managing and healing shoulder injuries. These include:
- Physical therapy, which aims to restore mobility and strength to the injured shoulder.
- Applying ice packs to reduce pain and swelling.
- Incorporating ergonomic tools to prevent further strain.
- NSAIDs for pain and inflammation reduction.
- Maintaining proper posture during activities to support recovery.
Additionally, for some injuries, corticosteroid or PRP injections may be offered to provide temporary pain relief and reduce inflammation in the shoulder joint. These conservative treatments aim to ease shoulder pain and promote healing.
Surgical Interventions
For severe shoulder injuries or conditions that do not respond to nonsurgical treatments, surgical intervention may be recommended. Arthroscopic repair, a minimally invasive procedure, involves using small incisions and specialized tools to repair damage. For some shoulder conditions, shoulder replacement may be a surgical option. Recovery expectations can vary based on the type of surgery and the patient’s overall health.
Preventing Future Shoulder Injuries
Following preventive measures can be helpful in overall shoulder health and functionality, reducing the risk of future injury. Next, we will explore specific strategies, including strengthening exercises, avoiding overuse, and using proper techniques and equipment.
Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening exercises can help enhance shoulder stability. Exercises that can support the stabilizing muscles include resistance band work, lateral raises, arm circles, and wall slides. These exercises not only build strength but also can improve flexibility, helping the shoulder prepare to handle various movements and activities with a lower risk of injury.
Avoiding Overuse
Overuse injuries are common in individuals who engage in repetitive shoulder movements without adequate rest. Regular breaks during activities are important to prevent overuse injuries and maintain shoulder health. Incorporating these breaks into your routine can reduce the risk of developing overuse injuries.
Proper Technique and Equipment
Proper techniques and equipment during sports and daily activities can help prevent common sports injuries and shoulder injuries. Employing correct techniques can reduce undue stress on the shoulder joint, while using appropriate sports gear and protective equipment can help maintain shoulder safety.
Summary
Shoulder injuries vary in recovery time, from weeks for mild sprains to many months or even a year for severe rotator cuff tears. Recovery depends on age, injury severity, and treatment adherence. Rehabilitation typically plays a key role after both nonsurgical and surgical treatments, and preventive measures such as strengthening, avoiding overuse, and using proper technique can help protect against future injuries.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take for a rotator cuff tear to heal?
Recovery times can vary based on the severity of the injury. Healing may take several months, with minor tears often improving within weeks to months and severe tears taking up to a year.
What is the recovery time for a shoulder sprain?
The recovery time for a shoulder sprain can vary; mild sprains typically heal in a couple of weeks, while severe cases may require around six months for full recovery.
How does age affect shoulder injury recovery?
Younger individuals generally heal faster, while older adults may require longer recovery due to natural age-related changes such as decreased circulation or other health complications.
Are there nonsurgical treatments for shoulder injuries?
Yes, nonsurgical treatments for shoulder injuries include physical therapy, rest, ice, corticosteroid injections, and ergonomic adjustments. For some injuries, these treatment options can effectively manage and facilitate healing.
What role does rehabilitation play in shoulder injury recovery?
Rehabilitation typically plays an important role in recovery for many shoulder injuries as it can help restore range of motion, build strength, and prevent re-injury.





