Wondering if your shoulder pain might be a torn rotator cuff? This post explains how to tell if you have a torn rotator cuff, and what steps to take next for diagnosis and treatment.
Key Takeaways
- A torn rotator cuff can range from partial to complete tears, often resulting from acute trauma or gradual overuse, significantly impacting shoulder functionality.
- Key symptoms of a torn rotator cuff include persistent shoulder pain, difficulty lifting or moving the arm, and swelling or tenderness in the shoulder area.
- Treatment options vary from conservative methods like physical therapy and corticosteroid injections to surgical interventions for severe tears, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and intervention.
What is a Rotator Cuff Tear?
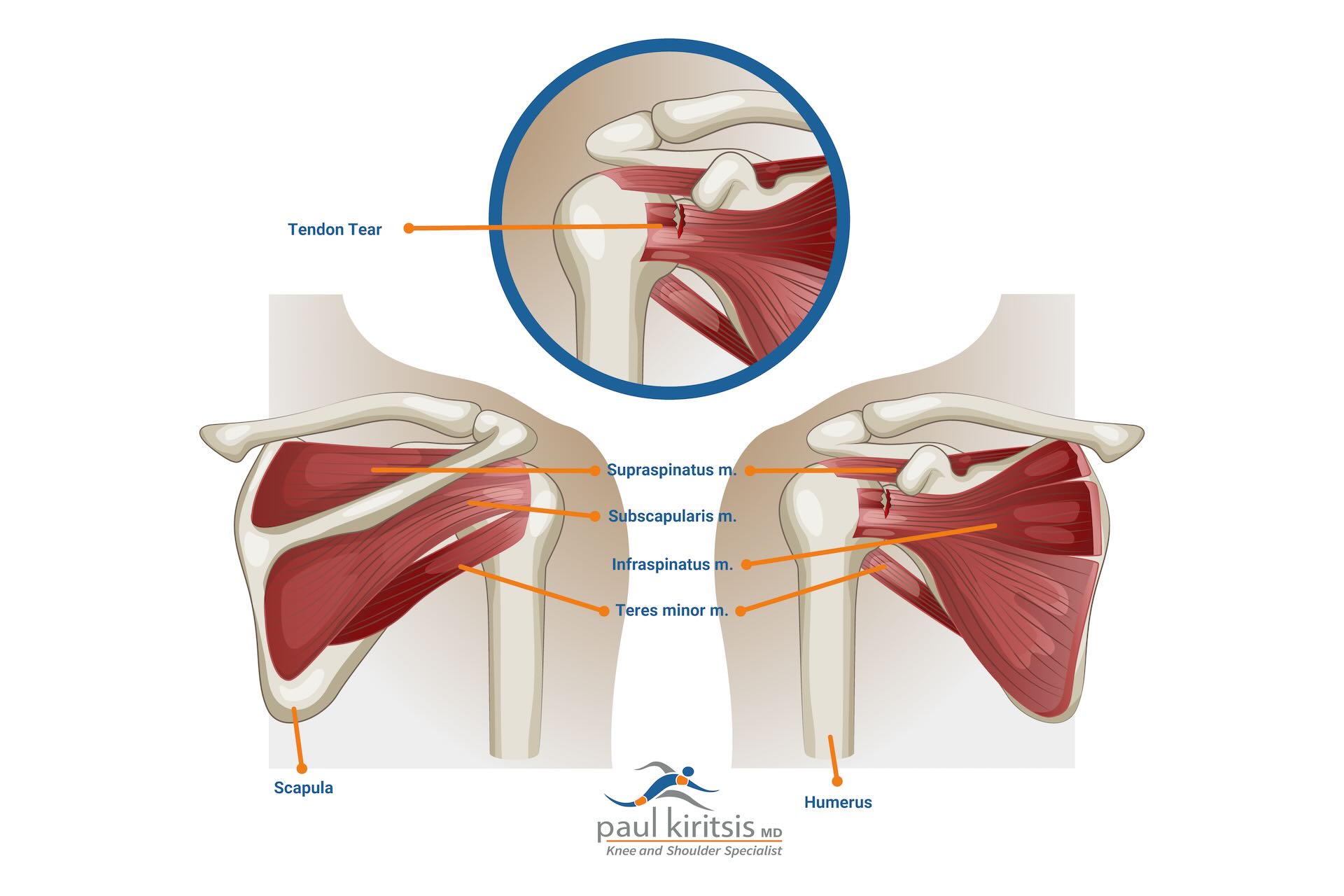
A rotator cuff tear is an injury involving the tendons of the rotator cuff muscles, which can result in either partial or complete tendon tears. Many rotator cuff injuries can severely impair shoulder functionality, making everyday tasks challenging. The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint, allowing for a wide range of movements including lifting and rotating the arm. Most rotator cuff tears involve the supraspinatus tendon, but other rotator cuff tendons can also be affected.
Rotator cuff tears can be categorized as either partial tear or complete tear, depending on the extent of the detachment. Acute tears often result from traumatic events like a fall or lifting a heavy object, while a degenerative tear develops gradually over time due to repetitive use or wear and tear. A full thickness tear is one of the types of rotator cuff tears. Knowing the causes and types of rotator cuff tears helps in identifying and addressing the problem effectively.
Key Symptoms of a Torn Rotator Cuff
Early identification of a torn rotator cuff is important for effective treatment and recovery. Common symptoms include persistent shoulder pain, difficulty lifting or moving the arm, audible sounds from the shoulder, swelling and tenderness, decreased range of motion, arm weakness, rotator cuff problems, and rotator cuff tear symptoms.
These symptoms can prompt timely medical intervention, ensuring better shoulder health.
Persistent Shoulder Pain
One of the most telling signs of a rotator cuff tear is persistent shoulder pain. This pain often manifests as a dull, deep ache that worsens at night, especially when lying on the affected shoulder. Many individuals report that the pain becomes more intense at night, making it difficult to find a comfortable sleeping position. This persistent pain is not just a minor inconvenience; it can significantly impact your quality of life, disrupting sleep and daily activities.
Experiencing shoulder pain that does not improve with rest is a significant indicator of potential rotator cuff issues. If you find yourself waking up due to shoulder pain or unable to perform routine tasks without discomfort, it may be time to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation.
Difficulty Lifting or Moving the Arm
A torn rotator cuff can severely limit your ability to lift or move your arm. This difficulty often presents as pain and weakness, making simple tasks like reaching overhead or behind your back challenging. If you notice that lifting your arm causes significant discomfort or that you can’t move it as freely as before, it could be a sign of a rotator cuff tear.
Arm weakness is another common symptom, and it can hinder your daily activities. Tasks that involve lifting or gripping objects may become difficult, affecting your ability to perform at work or engage in recreational activities. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to a timely diagnosis and reduce the risk of worsening weakness.
Audible Sounds from the Shoulder
Unusual sounds like popping, cracking, or clicking when moving your shoulder often indicate an underlying rotator cuff problem.
Consistently hearing these noises during shoulder movements warrants a check-up, as they can be symptoms of a rotator cuff tear.
Swelling and Tenderness
Swelling and tenderness around the shoulder are potential signs of a torn rotator cuff. This localized inflammation can cause significant discomfort and make the shoulder area sensitive to touch. It’s important to monitor these symptoms, as they can signal an injury that requires medical attention.
Early recognition of swelling and tenderness is important for effective treatment. Experiencing these symptoms along with shoulder pain and difficulty moving your arm should prompt a consultation with a healthcare professional. Early intervention can prevent further damage and aid in quicker recovery.
Decreased Range of Motion
A decreased active range of motion is a common symptom of rotator cuff damage. You may find it challenging to reach behind your back or lift objects overhead, which can significantly impact your daily life. This limitation in mobility is a clear indicator that something is wrong with your shoulder and should not be ignored. The shoulder is a ball and socket joint, which contributes to its wide range of motion.
Arm Weakness
Weakness in the arm is a prevalent symptom of a torn rotator cuff. This shoulder weakness can make everyday tasks, such as combing your hair or lifting objects, extremely difficult. If you notice a significant drop in your arm strength, it’s a sign that you should seek medical advice.
Arm weakness can also be accompanied by arm pain and arm weakness, further complicating movements and reducing your ability to perform routine activities. Addressing this symptom early on can lead to more effective treatment and a quicker return to your normal activities.
Diagnosing a Torn Rotator Cuff
Diagnosing a torn rotator cuff requires a combination of physical examinations and imaging techniques. During a physical exam, an orthopedic shoulder surgeon will assess muscle atrophy and scapular motion to determine the extent of the injury. Specific tests like the Neer and Hawkins tests are used to identify subacromial impingement, while the empty-can and full-can tests detect tears in the supraspinatus tendon.
Imaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), play a critical role in confirming the diagnosis and assessing the severity of the injury. These imaging tests provide detailed images of the shoulder joint, helping doctors to pinpoint the exact location and extent of the tear. Combined with physical examinations, they ensure an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Rotator Cuff Tears
Treatment options for rotator cuff tears vary depending on the severity of the injury, ranging from conservative methods to surgical interventions. The main goal is to safely and quickly return to normal activities.
Conservative Treatments
Conservative treatments for a torn rotator cuff include activity modification, ice application, and the use of slings to immobilize the shoulder. Physical therapy is one of the most effective non-surgical treatment options, focusing on strengthening the surrounding muscles and restoring shoulder functionality.
Oral pain relievers, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, are often recommended to manage mild pain. These conservative methods can be highly effective, especially for partial tears, and aim to alleviate pain and improve shoulder function through nonsurgical treatment without the need for surgery, particularly in the surrounding soft tissues.
Injections
Corticosteroid injections are commonly used to reduce inflammation and provide pain relief for those suffering from rotator cuff tears. These injections can significantly improve shoulder function, allowing patients to engage more effectively in physical therapy and daily activities.
For patients who are unable to undergo surgery or need effective pain management, a cortisone injection can be a valuable option. However, it’s important to note that while these injections provide temporary relief, they may not be a permanent solution and can weaken the tendon over time.
Biologics like PRP can be helpful in controlling pain and improving function in patients with rotator cuff symptoms.
Surgical Interventions
For severe rotator cuff tears, surgical interventions may be necessary. Minimally invasive arthroscopic procedures are the standard of care to repair torn rotator cuffs. These procedures are typically outpatient, and patients can expect a recovery time of 4 to 6 months for shoulder function and strength, with full recovery taking 12 months.
In very few cases where minimally invasive techniques are not suitable, open tendon repair may be required. For patients with massive rotator cuff tears, reverse shoulder replacement might be considered. The choice of surgical approach depends on the size and location of the tear, and it’s essential to discuss all options with an experienced orthopedic shoulder surgeon to recommend surgery as the best course of action for rotator cuff repair.
Preventing Rotator Cuff Injuries
Preventing rotator cuff injuries involves a combination of strengthening exercises, proper techniques, and adequate rest and recovery. By taking proactive steps to protect your shoulder health, you can significantly reduce the risk of experiencing a rotator cuff tear.
Strengthening Exercises
Regular strengthening exercises are key to preventing rotator cuff injuries. A comprehensive shoulder exercise regimen should target the shoulder muscles that retract the shoulder blade and strengthen the rotator cuff, helping to maintain shoulder strength and flexibility and reducing the risk of injury from everyday tasks.
Overhead activities and repetitive overhead movements significantly increase the risk of developing rotator cuff tears. Incorporating specific strengthening exercises into your routine enhances shoulder stability and prevents injuries.
Proper Techniques
Proper techniques during physical activities minimize the risk of rotator cuff injuries. Whether lifting weights, playing sports, or performing everyday tasks, maintaining proper form protects your shoulder from excessive strain.
Consistently applying correct techniques safeguards your shoulder health. Focusing on proper mechanics and avoiding improper lifting and overhead activities significantly reduces the likelihood of shoulder injuries.
Adequate Rest and Recovery
Adequate rest and recovery are essential for preventing overuse injuries, including rotator cuff tears and re tear. Incorporating recovery breaks during repetitive shoulder activities helps prevent chronic overuse injuries and allows your muscles and tendons to heal.
Resting the shoulder and applying ice can help alleviate symptoms if a rotator cuff injury is suspected.
Summary
Recognizing the symptoms of a torn rotator cuff early on can make a significant difference in your treatment and recovery process. Persistent shoulder pain, difficulty lifting or moving the arm, audible sounds, swelling, tenderness, decreased range of motion, and arm weakness are key indicators that should not be ignored.
By understanding the diagnostic process and exploring the various treatment options, from conservative methods to surgical interventions, you can make informed decisions about your shoulder health. Preventative measures, including strengthening exercises, proper techniques, and adequate rest, are essential for maintaining a healthy and functional shoulder.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of a torn rotator cuff?
Common symptoms of a torn rotator cuff include persistent shoulder pain, difficulty lifting or moving the arm, audible sounds from the shoulder, swelling, tenderness, decreased range of motion, and weakness in the arm. If you’re experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to consult an orthopedic surgeon who specializes in shoulders for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
How is a torn rotator cuff diagnosed?
A torn rotator cuff is diagnosed through physical examinations assessing muscle atrophy and scapular motion, specific tests like the Neer and Hawkins tests, and imaging techniques such as MRI. This comprehensive approach ensures an accurate diagnosis.
What are the treatment options for a torn rotator cuff?
For a torn rotator cuff, treatment options include conservative methods such as physical therapy and pain management, as well as surgical interventions like minimally invasive arthroscopic procedures and tendon repair, depending on the severity of the tear.
How can I prevent rotator cuff injuries?
To prevent rotator cuff injuries, focus on regular strengthening exercises, practice proper techniques during activities, and prioritize adequate rest and recovery to avoid overuse. These measures are essential for maintaining shoulder health.
What should I do if I suspect a rotator cuff tear?
If you suspect a rotator cuff tear, it is crucial to seek medical advice for a thorough evaluation and an appropriate treatment plan. This will help you avoid further damage and promote a quicker recovery.





