If you’re dealing with chondromalacia patella, you may wonder whether your daily walks are helping or hurting your knees. In this post, we’ll explore the benefits and risks of walking with this condition and discuss how to incorporate walking safely into your routine.
Key Takeaways
- Regular walking can relieve symptoms of chondromalacia patella by reducing stiffness, improving knee function, and promoting blood circulation.
- Proper walking techniques and precautions, such as avoiding stairs, wearing cushioned shoes, and walking on flat surfaces, are essential for managing knee pain.
- Incorporating alternative low-impact exercises like swimming and cycling into your routine can further support knee health and fitness while minimizing strain.
Understanding Chondromalacia Patella
Chondromalacia patella, a form of patellofemoral pain syndrome, is a condition characterized by the deterioration of the cartilage beneath the kneecap. The patella, or kneecap, plays an important role in the patellofemoral joint, and damage to the cartilage here can cause significant discomfort. This condition typically presents as pain at the front of the knee and sensitivity around the kneecap.
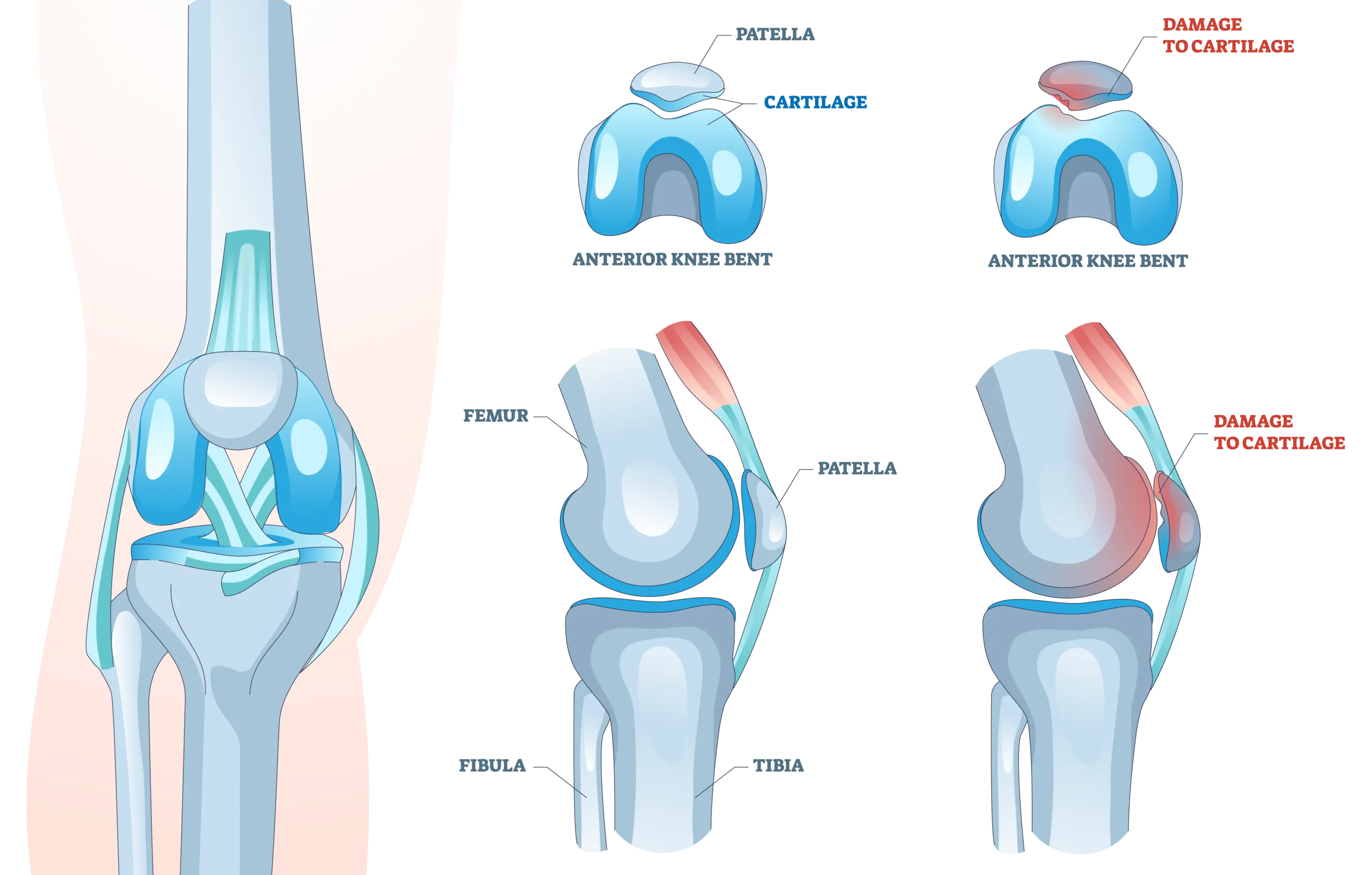
Common causes include repetitive stress or injury to the knee joint, especially in athletes and physically active individuals. Other contributing factors include anatomical misalignment and previous knee injuries, which can disrupt the smooth movement of the patella. Over time, inflammation and cartilage wear can worsen, leading to increased pain and limited knee function.
Diagnosing chondromalacia patella involves a thorough clinical evaluation, including a physical examination and imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, or arthroscopy. Understanding the condition and its underlying causes is essential for developing an effective treatment plan, which may include conservative measures like physical therapy or, in more advanced cases, surgical intervention.
The Benefits of Walking for Chondromalacia Patella
When done with care, regular walking can be beneficial for managing chondromalacia patella. It may help:
- Reduce stiffness
- Decrease inflammation
- Improve overall knee function, making it easier to perform daily activities
- Encourage blood flow to the knee, supporting cartilage healing
Another benefit of walking is weight management. Maintaining a healthy weight minimizes the pressure on the knees, reducing pain and preventing further cartilage damage. Walking offers a simple yet effective way to alleviate the excess burden on your knees without engaging in high-impact activities that could further irritate the joint.
Additionally, walking helps preserve joint mobility. Keeping the knee in motion helps prevent stiffness and maintain functional range of motion. When performed properly and with necessary precautions, walking can serve as a foundational low-impact exercise to support overall knee health.
How to Walk Properly with Chondromalacia Patella
Using proper walking techniques can make a significant difference in managing knee pain associated with chondromalacia patella.
Maintaining correct posture helps maintain joint alignment, reducing stress on the knees and allowing the patella to glide smoothly over the thigh bone (femur). Additionally, choosing smooth and flat surfaces for walking further reduces impact, helping to prevent irritation and discomfort.
Engaging your core muscles while walking can provide better stability and support for the knee. This not only helps in maintaining balance but also reduces the load on the knees, making each step less painful. Incorporating the quadriceps and gluteal muscles during walking can enhance stability and support. Consciously focus on your stride and activate these muscles with each step. Strengthening these muscle groups also addresses imbalances and improves control of knee movement, especially when walking with a straight leg.
It’s also important to maintain a moderate pace and avoid abrupt starts or stops. By following these guidelines, you can gain the benefits of walking while minimizing the risks associated with chondromalacia patella.
Precautions to Take While Walking
Taking the right precautions can help minimize discomfort and reduce pain while walking. Key recommendations include the following:
- Minimize stair climbing, which places excessive pressure on the kneecap
- Avoid deep squats and kneeling, both of which can irritate the joint and worsen symptoms
- Consider using a walking stick or cane as needed to reduce the load on the affected leg and improve balance
- Choose well-cushioned shoes that absorb shock and protect the knee from unnecessary stress
By taking these precautions, you can reduce the risk of aggravating your symptoms and ensure that walking remains a safe and effective part of your chondromalacia patella management plan.
Alternative Low-Impact Exercises
Engaging in alternative low-impact chondromalacia exercises can significantly assist in managing chondromalacia patella symptoms. Water-based activities, such as swimming and water aerobics, are advantageous as they allow for resistance training without putting weight on the knees. Water aerobics, in particular, provides strength training, cardiovascular benefits, and is low-impact on joints, making it ideal for those with chondromalacia patella.
Cycling on flat terrain is another excellent choice, as it promotes cardiovascular health and strengthens the legs with minimal impact on the knees. Rowing also provides a low-impact, full-body workout that avoids direct stress on the joint. Additionally, yoga can help improve flexibility, balance, and muscular strength, all of which support proper knee alignment and function.
Elliptical training and closed-chain exercises (such as leg presses, where the feet stay in contact with a stable surface) are also useful for building strength without overloading the joint. When incorporated thoughtfully, these low-impact exercises can preserve knee health and support a sustainable, joint-friendly fitness routine.
Activities to Avoid with Chondromalacia Patella
High-impact activities can worsen the symptoms of chondromalacia patella and should generally be avoided. These movements place excessive pressure on the kneecap and can accelerate cartilage deterioration. To prevent further irritation and pain, patients are typically advised to avoid squatting, kneeling, and exercises that strain the kneecap.
In addition, activities that involve jumping or sudden, forceful movements can aggravate symptoms. Avoiding these types of activities is important for reducing inflammation, protecting the joint, and supporting long-term recovery.
Additional Treatment Options
Conservative treatment approaches are often the first step in managing chondromalacia patella. These treatments typically include rest, physical therapy, and pain management medications. The goal of these treatments is to reduce inflammation, strengthen the muscles, and manage pain.
If conservative measures fail to provide relief, surgical options may be considered. These options may include arthroscopy, a minimally invasive procedure where damaged cartilage may be removed, and realignment procedures, which adjust the position of the kneecap to reduce pressure on cartilage.
An experienced orthopedic surgeon can guide you through a treatment plan that addresses your specific needs and symptoms. A personalized approach ensures you receive appropriate care to reduce pain, restore function, and prevent further joint damage.
Summary
In summary, walking can be a beneficial exercise for managing chondromalacia patella, as long as it’s done using proper form and precautions. By maintaining a moderate pace, choosing flat surfaces, and engaging the core, you can reduce knee pain and improve joint mobility. Complementing walking with alternative low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, and yoga can further support knee health.
Working closely with a knee specialist and adhering to their guidance is essential for effective management of chondromalacia patella. By staying proactive and mindful of your activities, you can alleviate pain and enhance your quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is chondromalacia patella?
Chondromalacia patella involves the deterioration of cartilage beneath the kneecap, leading to pain and dysfunction. It’s important to seek a diagnosis and appropriate treatment to manage symptoms effectively.
Is it okay to walk with chondromalacia patella?
Walking can be a good low-impact exercise for chondromalacia patella, as long as it’s done with proper form and precautions. Walking can help reduce joint stiffness, improve blood circulation, and support overall knee function. If pain increases during or after walking, consider consulting your doctor to adjust your routine.
What are the common causes of chondromalacia patella?
Chondromalacia patella is commonly caused by repetitive stress on the knee, prior injuries, or anatomical factors that affect patellar alignment.
How is chondromalacia patella diagnosed?
Chondromalacia patella is diagnosed through a comprehensive clinical evaluation that includes patient history and physical examination, often confirmed by imaging tests like X-rays or MRI. Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment and management of the condition.
What are the main symptoms of chondromalacia patella?
The main symptoms of chondromalacia patella are anterior knee pain, swelling, a grating or grinding sensation, and increased pain during activities such as climbing stairs or squatting. These indicators suggest the need for proper assessment and management.
What are the treatment options for chondromalacia patella?
The primary treatment options for chondromalacia patella focus on conservative management, including physical therapy and medications, while surgical interventions may be pursued if these methods do not provide relief.





